

Sunday, February 14, 2010
| Electricity and Water If your hands tingle when you put them into the sink it may mean the water is conducting electricity and something is wrong. Let an adult know, as they may need to call an electrician. When you have a bath, there should be nothing electrical anywhere near you. In a bath, the metal plughole and the plumbing is connected to the earth, making it a conductor of electricity. This means if a household appliance such as a light or hair dryer fell into the bath, whoever was in it would also become a conductor of electricity. Wherever you are, if you get into trouble call out for help and make sure not to touch anything. Get whoever helps you to turn the electricity of | |
| Water can conduct electricity because electrons can flow by hitching a ride on atoms and molecules in the water. Water contains dissolved substances, such as salt. These greatly increase the ability of water to conduct electricity. That's why electricity passes easily through our bodies - because our bodies contain water and salt. This is also why it's important to keep water away from electrical appliances. | |
If you fly a kite and it gets caught in the overhead powerlines, live electricity could travel down the string and seriously hurt you. So be careful. |  |
| We all like to play outside, but there are electrical hazards that we need to know about. Electricity poles and wires are all around us. They can be above us, next to us, and even below us. Whenever you can, play in open spaces away from electricity poles, towers and powerlines. | |
| Never put a metal object - like a knife - into a toaster. It is very dangerous! Never put anything in a power point that's not meant for it, especially if the thing is metal. Electricity will travel right up the metal object into your body. Be careful when climbing a ladder at home. The power lines connected to our house are usually protected, but they can be damaged by rubbing against the gutter or a tree, or through exposure to the sun. If a person is on a metal ladder and touches the exposed line, the electricity will travel through their body to the earth. | |
| We all come into contact with metal objects on a daily basis - turning on a tap, using our computers and even opening the fridge. Because metal conducts electricity, you have to be very careful when you use metal items. | |
| Faulty appliances and damaged electrical leads should be disconnected at the power point and fixed or replaced by an electrician. Never stack power points. Use a power board or have an extra power point installed. Stacked power points can cause fires. | |
| Always be on the look out for dangers in and around your home. This could be anything from a faulty electrical lead to a "stacked" power point - one with too many plugs in it. These situations could be life threatening and an electrician should be called in to fix them. | |
Friday, February 12, 2010
Power is the rate at which work is performed or energy is converted. It is an energy per unit of time. As a rate of change of work done or the energy of a subsystem, power is

where P is power, W is work and t is time.
The SI unit of power is the watt (W), which is equal to one joule per second.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_%28physics%29
Thursday, February 11, 2010


 To make a current flow through a resistance there must be a voltage across that resistance. Ohm's Law shows the relationship between the voltage (V), current (I) and resistance (R). It can be written in three ways:
To make a current flow through a resistance there must be a voltage across that resistance. Ohm's Law shows the relationship between the voltage (V), current (I) and resistance (R). It can be written in three ways: | V = I × R | or |
| or |
|
| where: | V = voltage in volts (V) I = current in amps (A) R = resistance in ohms ( | or: | V = voltage in volts (V) I = current in milliamps (mA) R = resistance in kilohms (k |
The Ohm's Law equations work if you use V, A and ![]() , or if you use V, mA and k
, or if you use V, mA and k![]() . You must not mix these sets of units in the equations so you may need to convert between mA and A or k
. You must not mix these sets of units in the equations so you may need to convert between mA and A or k![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Tuesday, February 9, 2010
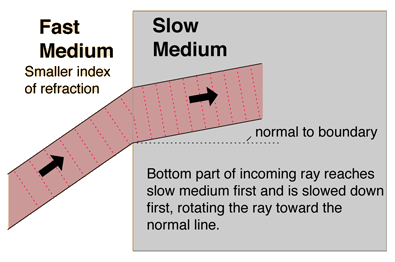
Most of that refraction in the eye takes place at the first surface, since the transition from the air into the cornea is the largest change in index of refraction which the light experiences. About 80% of the refraction occurs in the cornea and about 20% in the inner crystalline lens.
While the inner lens is the smaller portion of the refraction, it is the total source of the ability to accommodate the focus of the eye for the viewing of close objects. For the normal eye, the inner lens can change the total focal length of the eye by 7-8%.
Common eye defects are often called "refractive errors" and they can usually be corrected by relatively simple compensating lenses.
short video showing refraction in a crystal ball:
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu
Reflection is the bouncing back of a light ray from a surface.
Law of Reflection
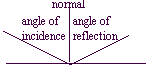
When a light ray is incident upon a reflecting surface, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. Both of these angles are measured relative to a normal drawn to the surface. The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane.
Diffused reflection
Regular reflection
Types of mirrors:
Type of images:
Characteristics of plane mirror images:
Steps for drawing a plane mirror ray diagram: